
Introduction
Back-end development is the backbone of any website or web application, handling the logic, database interactions, and server-side operations that allow the front-end to function seamlessly. Without robust back-end systems, websites would struggle to serve dynamic content, manage user data, or execute business logic effectively. This guide delves into back-end development's core principles, exploring the technologies, skills, and best practices that form the foundation of today’s high-performing digital platforms.
Table of Contents
- What is Back-End Development?
- Back-End vs. Front-End Development
- Core Back-End Technologies
- Back-End Architecture Patterns
- Key Back-End Frameworks
- APIs and Communication
- Database Management
- Security in Back-End Development
- Scalability and Performance Optimization
- Best Practices in Back-End Development
- Tools for Effective Back-End Development
- Back-End Development Career Paths
- Emerging Trends in Back-End Development
- Challenges in Back-End Development
- Future of Back-End Development
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Back-End Development?
Back-end development, often termed the backbone of digital applications, involves building the server-side logic and infrastructure that power websites, apps, and digital services. Back-end developers are responsible for creating the systems that manage data storage, processing, and retrieval, ensuring reliable performance for end users. Their work includes managing databases, servers, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that link the front-end (user-facing) elements with core functionalities.
Back-end development is crucial in industries where complex data interactions or highly secure transactions are needed. From online banking platforms to e-commerce websites, robust back-end systems allow for reliable, scalable, and secure applications. While front-end development deals with the visual elements that users see, the back end is essential for providing functionality, security, and data integrity.
Back-End vs. Front-End Development
Front-end development involves creating the user interface and interactive elements that customers engage with, while back-end development supports these functions by managing the underlying infrastructure and data flow.
Differences in Skills and Tools
Front-end developers use languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create responsive designs, whereas back-end developers work with server-side languages such as Python, Java, and PHP. Front-end focuses on design aesthetics and user experience, while back-end emphasizes data management, security, and performance.Collaboration Between Front-End and Back-End
Seamless collaboration between front-end and back-end developers is essential for delivering a smooth user experience. Back-end teams provide APIs and data endpoints for front-end developers to pull information from, ensuring consistent data display and interaction across devices.
Core Back-End Technologies
Back-end developers work with a variety of technologies to manage the logic and infrastructure behind a web application. Some of the most critical technologies include:
- Programming Languages: Common languages for back-end development include Python, Java, JavaScript (Node.js), Ruby, PHP, and C#. Each language offers unique advantages and is suited to specific project needs.
- Databases: Managing data is a central responsibility in back-end development. Commonly used databases include relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL, as well as NoSQL options like MongoDB and Cassandra, each offering specific benefits based on application needs.
- Server Technologies: Web servers, such as Apache, Nginx, and IIS, serve as the foundation for hosting and delivering back-end content. Cloud-based servers from AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure also play a significant role in scalable applications.
Back-End Architecture Patterns
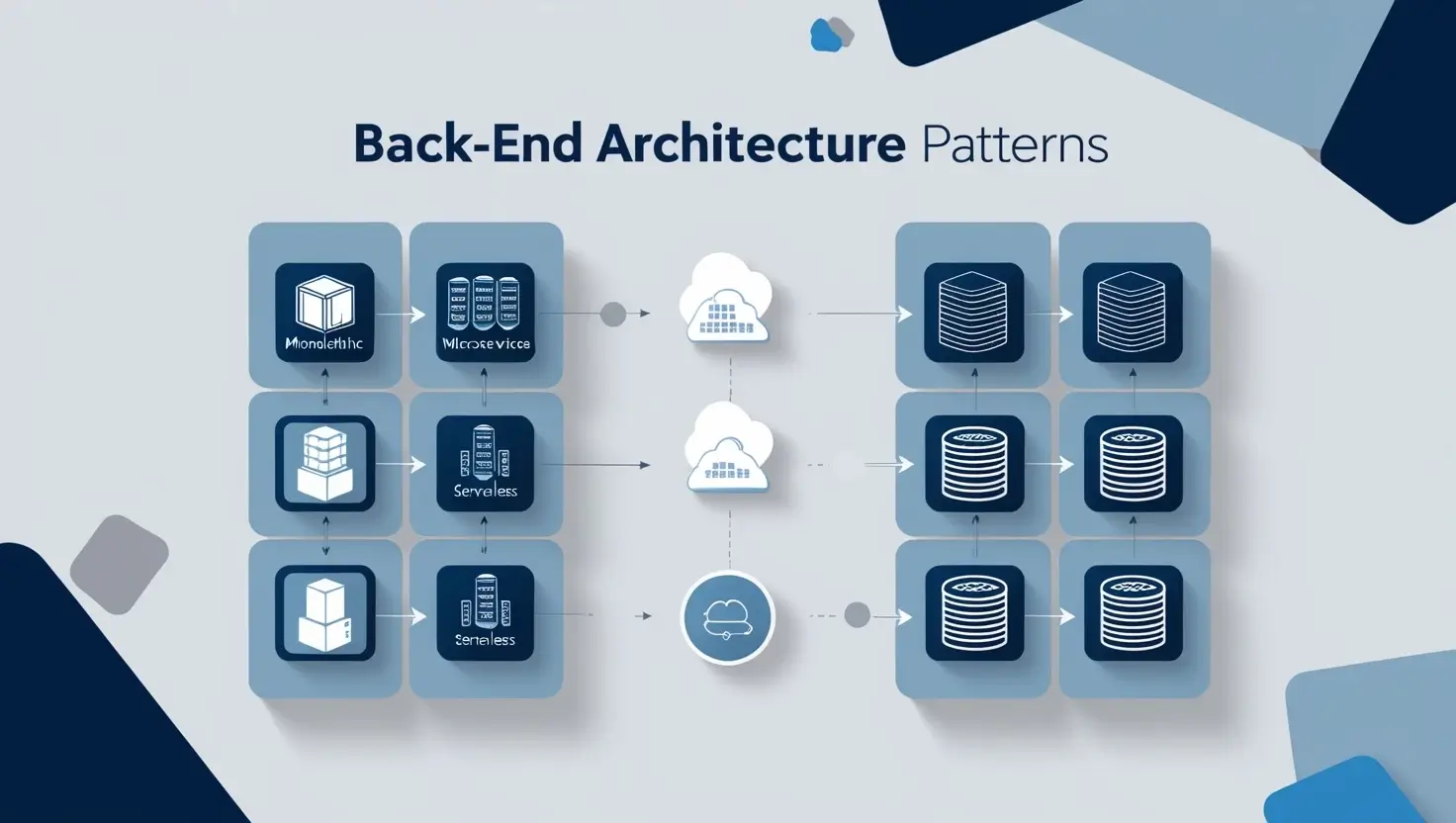
Different architectural patterns help developers structure applications for performance and scalability:
- Monolithic Architecture: A single, unified codebase where all components are interconnected. Suitable for smaller applications, it can become complex as the application scales.
- Microservices Architecture: An application is divided into small, independent services. This structure supports greater scalability and flexibility, especially for large, complex applications.
- Serverless Architecture: Serverless abstracts the infrastructure, allowing developers to focus solely on code. This pattern is useful for applications with variable or unpredictable traffic.
Each pattern comes with advantages and challenges, with the right choice depending on the project's size, scale, and maintenance needs.
Key Back-End Frameworks
Frameworks simplify the coding process by providing pre-built components for common functions like database connections, routing, and user authentication. Here are four popular frameworks that have distinct advantages in back-end development. Choosing the right framework can significantly impact development speed, security, and scalability:
Node.js: Node.js allows JavaScript developers to write server-side code, making it ideal for full-stack JavaScript applications. Its asynchronous nature enables it to handle high-traffic applications efficiently.
Django: Django, a Python-based framework, is known for its simplicity and robustness, making it popular among developers focused on rapid development and scalability.
Ruby on Rails: Known for its convention-over-configuration philosophy, Ruby on Rails is ideal for rapid application development and is often used for MVPs (Minimum Viable Products). Each framework offers a set of tools, libraries, and best practices that help developers build secure, scalable, and maintainable applications.
Laravel: Laravel is a powerful PHP framework known for its elegant syntax and ease of use. Built on the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture, Laravel streamlines tasks like routing, authentication, and caching. With a strong ecosystem, including tools like Laravel Forge and Laravel Vapor for deployment, this framework offers everything needed to build modern, maintainable applications. Its intuitive design and extensive documentation make Laravel accessible for both beginners and seasoned developers.
Node.js: Asynchronous Back-End Framework

Overview of Node.js
Node.js is a JavaScript runtime environment that allows developers to use JavaScript for both front-end and back-end development. With its asynchronous, non-blocking nature, Node.js excels in handling large volumes of simultaneous requests, making it ideal for real-time applications like chat apps or online games.Advantages of Node.js
Node.js uses a single-threaded event loop, which makes it efficient for I/O-heavy operations. Additionally, its compatibility with JavaScript and access to npm (Node Package Manager) offers a vast selection of libraries and tools, enabling developers to streamline application development.
Popular Applications of Node.js
Popular companies like Netflix, LinkedIn, and Uber use Node.js to build scalable, high-performance applications. Its speed and scalability make it a preferred choice for applications requiring real-time data updates.
Django: High-Level Python Framework

Introduction to Django
Django, a high-level Python framework, is known for its emphasis on simplicity and security. Django’s “batteries-included” philosophy provides developers with tools for rapid development, including an ORM (Object-Relational Mapping), authentication modules, and form handling.
Benefits of Using Django
One of Django’s standout features is its security capabilities, with built-in defenses against SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and cross-site request forgery. Django’s ORM and migrations allow developers to interact with databases using Python code, promoting efficiency in complex applications.
Django’s Use in Web Development
Django is used by organizations like Instagram, Pinterest, and Mozilla for its ease of use and flexibility. Its robust framework and modular components allow developers to create scalable applications quickly.
Ruby on Rails: Developer-Friendly Framework
What is Ruby on Rails?
Ruby on Rails (Rails) is a popular open-source framework built on the Ruby language. It follows the convention-over-configuration principle, reducing the number of decisions developers must make and allowing for quick development.Advantages of Ruby on Rails
Rails is designed for developer productivity and offers built-in tools for routing, ORM, and form validations. This framework allows for the development of applications that can scale as businesses grow, making it ideal for startups and small businesses.
Who Uses Ruby on Rails?
Ruby on Rails is used by platforms like GitHub, Shopify, and Airbnb. Its intuitive framework and active community support make it an appealing choice for developers seeking a rapid yet structured approach to web development.
Laravel: PHP Framework for Elegant Coding

Laravel Overview
Laravel is a PHP framework renowned for its elegant syntax and ease of use. It follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architectural pattern, offering clean separation between data, logic, and presentation.
Key Features of Laravel
Laravel simplifies tasks like routing, sessions, and caching, making it developer-friendly. Its Eloquent ORM allows developers to interact with databases in an expressive, easy-to-read syntax. Laravel’s built-in testing features further enhance development efficiency.
Laravel’s Role in Web Applications
Laravel is a preferred choice for small to medium-sized businesses and startups, with applications in e-commerce and content management systems. Its comprehensive documentation and strong community make it an accessible framework for new developers.APIs and Communication
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are essential for communication between the front end and back end:
- REST APIs: The most common API style, REST is easy to use, making it ideal for CRUD operations and simple applications.
- GraphQL: A more flexible alternative to REST, GraphQL allows clients to request only the data they need, which optimizes bandwidth and speeds up response times.
- WebSockets: WebSockets enable two-way communication and are useful for real-time applications such as chat platforms and live streaming services.
APIs play a crucial role in enabling scalable, interactive applications by facilitating efficient data exchange.
Database Management

Databases store and organize the data that applications rely on, and back-end developers need to choose the right type based on application requirements:
- SQL Databases: SQL databases (like MySQL, PostgreSQL) use structured query language and are known for reliability and support for complex queries. They are ideal for applications needing strong data integrity.
- NoSQL Databases: NoSQL options like MongoDB and Redis offer flexible data models, making them suitable for unstructured data and high-velocity, large-scale applications.
- Hybrid Approaches: Some applications use a combination of SQL and NoSQL databases to balance flexibility, scalability, and integrity.
Database management is a foundational skill in back-end development, with each type offering specific advantages depending on the project's demands.
Security in Back-End Development

In an era where data breaches and cyberattacks are frequent, back-end security is essential for safeguarding user data and system integrity. Security measures in back-end development include encryption, access controls, and coding practices to prevent vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS).
- Preventing Common Vulnerabilities: Securing the back end requires identifying and mitigating common vulnerabilities. Techniques like input validation, parameterized queries, and Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) protection help safeguard against common threats. Regular security audits, penetration testing, and keeping frameworks updated are all essential practices in a secure back-end environment.
- Data Encryption and Secure Connections: Encryption ensures that data transmitted between clients and servers remains private and secure. Using HTTPS and SSL/TLS certificates helps protect data from being intercepted or tampered with during transmission. Additionally, hashing sensitive information, such as passwords, ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains unreadable.
- Authentication and Access Control: Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) ensures that users can only access resources and actions for which they have permission. Using token-based authentication systems, such as OAuth or JWT, allows users to authenticate securely and prevents unauthorized access to sensitive areas of an application.
Back-end developers need to prioritize security practices, especially as data breaches become increasingly common.
Scalability and Performance Optimization

Scaling a back-end system involves ensuring that an application can handle increased traffic and data load efficiently. Scalability enables applications to serve a growing number of users while maintaining performance, reliability, and cost-efficiency.
- Vertical and Horizontal Scaling: Vertical scaling, or scaling up, adds resources (CPU, RAM) to a single server to increase its capacity. Horizontal scaling, or scaling out, involves adding more servers to distribute the load. Horizontal scaling is typically more cost-effective and allows for high availability and redundancy, especially when used with cloud providers like AWS and Google Cloud.
- Load Balancing and Caching: Load balancers distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from being overwhelmed. By distributing the load, applications can handle more requests while minimizing latency. Caching, which stores frequently accessed data, can further improve performance by reducing the number of database queries, leading to faster response times for end users.
- Database Optimization and Data Partitioning: Databases can be optimized through indexing, query optimization, and data partitioning techniques like sharding. Sharding divides large datasets into smaller, manageable parts stored across different servers, reducing the load on any single database and increasing the application’s overall capacity.
Scalability and optimization techniques are essential in back-end development to ensure applications can handle growth.
Best Practices in Back-End Development

Adhering to best practices in back-end development enhances code quality, maintainability, and team collaboration. Key practices include following coding standards, conducting code reviews, maintaining proper documentation, and testing rigorously.
Coding Standards and Clean Code
Using coding standards helps developers create readable and consistent code. Clean code principles encourage simplicity, clarity, and structure, which makes the codebase easier to understand and maintain. Naming conventions, modular coding, and avoiding redundancy are integral to writing clean, professional code.
Code Reviews and Peer Feedback
Code reviews help improve code quality by identifying issues and inefficiencies early on. Through peer reviews, team members can share knowledge, suggest improvements, and ensure that the code adheres to project standards. A regular code review process can prevent bugs and improve collaboration within development teams.
Documentation and Automated Testing
Comprehensive documentation is critical for the sustainability of a project. It allows new team members to understand the codebase and helps maintain functionality over time. Automated testing, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests, ensures that code performs as expected and reduces the likelihood of bugs during development and after deployment.
Tools for Effective Back-End Development

Back-end developers rely on various tools for code versioning, testing, deployment, and project management to streamline the development process and improve productivity.
Version Control Systems
Version control systems like Git, along with platforms like GitHub and GitLab, enable developers to track code changes, collaborate effectively, and manage code versions. They are essential for team projects, allowing multiple developers to work on the same codebase without conflicts.
Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
CI/CD tools, such as Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitHub Actions, automate the process of testing and deploying code. They help streamline development cycles, allowing developers to catch issues early and ensure that code is deployable at all times. CI/CD pipelines save time, reduce errors, and help teams release updates frequently and reliably.
Popular Back-End Development Tools
- Docker: Containerizes applications for consistency across environments.
- Postman: Useful for testing APIs by simulating client requests and validating responses.
- Redis: Provides in-memory data storage for faster access, often used for caching.
- Nginx: A popular web server that can also be used as a load balancer, improving traffic distribution.
Building a Career in Back-End Development
The demand for back-end developers is steadily rising, making it a lucrative and fulfilling career path for those with a passion for server-side development. Here’s what you need to know about skills, roles, career progression, and salary expectations.
Essential Skills for Back-End Developers
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in languages such as Python, Java, Ruby, and PHP is crucial, along with understanding databases and SQL/NoSQL management.
- Problem-Solving and Logical Thinking: The back end requires solid analytical skills to build efficient, bug-free applications.
- APIs and Frameworks: Knowledge of popular frameworks like Django, Node.js, Ruby on Rails, and Laravel, along with API development (RESTful, GraphQL), is valuable.
- Version Control and CI/CD: Familiarity with Git, GitHub, CI/CD practices, and deployment tools is essential for effective code management.
Job Roles and Career Paths
Back-end developers have a variety of career progression opportunities:
- Junior Back-End Developer: Entry-level role, focusing on building server-side applications.
- Senior Back-End Developer: Advanced responsibilities include architecting complex systems and mentoring junior developers.
- Full-Stack Developer: Combines both front-end and back-end skills, providing end-to-end solutions.
- DevOps Engineer: Specializes in CI/CD, deployment, and maintaining infrastructure for scalable applications.
- Solutions Architect: Designs complex systems, ensuring scalability, security, and cost-efficiency.
Salary Expectations and Certifications
Salaries for back-end developers vary by region, skill level, and experience. Entry-level salaries typically start around $60,000 per year, while experienced professionals can earn over $120,000 annually in high-demand regions like North America.
Certifications and Professional Development
Certifications can enhance credibility and knowledge in specific areas of back-end development. Examples include AWS Certified Solutions Architect, Microsoft Certified Azure Developer, and Google Professional Cloud Developer. These certifications demonstrate expertise in cloud and infrastructure management, which are invaluable in back-end roles.
Emerging Trends in Back-End Development

The back-end development landscape is continually evolving, driven by new technologies, demand for efficiency, and industry trends.
AI Integration in Back-End Development
AI is increasingly integrated into back-end systems, enabling automation of repetitive tasks and enhancing data analytics capabilities. For example, machine learning models can be deployed server-side to deliver real-time predictions and insights, enhancing application functionality and user experience.
Serverless Computing
Serverless architecture allows developers to run code without managing servers, enabling automatic scaling and reducing operational costs. Platforms like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions allow developers to focus on code rather than infrastructure, making serverless an appealing choice for modern back-end systems.
DevOps for Enhanced Collaboration
The integration of DevOps practices into back-end development has transformed software development. CI/CD pipelines, containerization, and automated testing streamline the development process, resulting in faster, more reliable releases. Back-end developers adopting DevOps methodologies can improve collaboration and deliver higher-quality applications.
Challenges in Back-End Development

Back-end development comes with unique challenges that can impact project timelines and functionality if not managed properly. Below are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them.
Performance Optimization
Efficiently managing server resources to handle high volumes of requests and complex computations is essential. Techniques like caching, database indexing, and load balancing can mitigate bottlenecks and enhance application responsiveness.
Data Security and Compliance
Security remains a top challenge as data breaches and cyberattacks become more sophisticated. Ensuring data encryption, implementing strict access control, and complying with data regulations (such as GDPR) are critical for back-end developers.
Scalability and Resource Management
Scaling a back-end system is complex, requiring careful planning of resource allocation and load management. Using cloud services and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes can streamline scaling and resource management, helping back-end systems handle fluctuating demands.
Keeping Up with Technology Advancements
Back-end developers must continuously adapt to new tools, languages, and best practices. Attending industry events, engaging in developer communities, and taking relevant certifications help developers stay up-to-date.
Future of Back-End Development
The future of back-end development is bright, with significant advancements anticipated in AI, data security, and the shift toward microservices and serverless architecture.
Increased AI and Automation
Artificial Intelligence is expected to drive back-end development, with increased automation of server-side tasks and improved data handling. AI-driven analytics and personalized content are likely to become standard, pushing back-end developers to incorporate machine learning models directly into applications.
Emphasis on Data Privacy and Security
As data regulations continue to evolve, back-end systems will need advanced security measures and data privacy compliance. Techniques such as multi-factor authentication, advanced encryption, and zero-trust architecture will likely become widespread to ensure compliance and prevent cyber threats.
Continued Growth of Serverless and Microservices Architectures
Serverless computing and microservices architectures are transforming the way applications are built and scaled. These architectures provide modular, scalable, and fault-tolerant systems that can handle diverse and growing data needs. Future back-end development will likely prioritize these architectures, enabling applications to adapt to user demands in real time.
Conclusion
Back-end development is the foundation of a web application, ensuring seamless operation, robust data handling, and scalable performance. By mastering back-end technologies, frameworks, architecture patterns, and best practices, developers can build high-performing, secure applications that provide excellent user experiences.
Back-end development is essential for creating robust, efficient, and scalable applications. With tools and frameworks like Node.js, Django, Ruby on Rails, and Laravel, developers can build secure, high-performance systems that support dynamic user experiences. By understanding back-end fundamentals, selecting the right tools, and following best practices, aspiring developers can excel in this critical field.
FAQ

Q1: What is the role of a back-end developer?
Back-end developers handle server-side logic, database management, and API integration, enabling front-end interfaces to function seamlessly.
Q2: What skills do I need to become a back-end developer?
To become a back-end developer, you should be proficient in a back-end language (like Python, Java, or Node.js), understand databases, and know about server and API management.
Q3: What’s the difference between front-end and back-end development?
Front-end development involves the user-facing side of a web application, while back-end development handles the server-side, data, and business logic.
Q4: What is the best back-end framework?
The best framework depends on the project’s needs. Node.js is ideal for real-time apps, Django is known for security, Ruby on Rails for rapid development, and Laravel for simplicity.
Q5: Which database is best for back-end development?
It depends on your application needs. SQL databases like MySQL are ideal for structured data, while NoSQL options like MongoDB work well for large-scale, unstructured data.
Q6: Is back-end development hard to learn?
Back-end development can be challenging, but with dedication and a structured learning approach, anyone can learn the necessary skills over time.
Q7: Why is API design important in back-end development?
APIs are crucial for facilitating data flow between client and server, allowing for a seamless user experience.
Q8: What is the difference between REST and GraphQL?
RESTful APIs provide data in a structured way, while GraphQL allows clients to request specific data, offering more flexibility.
Q9: How does back-end development relate to DevOps?
Back-end developers work closely with DevOps engineers to ensure the application runs smoothly, is easily deployable, and can scale efficiently.
Q10: What is the future of back-end development?
Back-end development continues to evolve with trends like serverless computing, microservices, and AI integration.
Q11: What is back-end security, and why is it important?
Back-end security involves practices to protect data and system integrity against unauthorized access and attacks. It’s crucial to safeguard user information and maintain trust in applications.
Q12: How does scalability benefit back-end development?
Scalability ensures that applications can handle increased traffic and data loads without compromising performance, supporting business growth and user demand.
Q13: What are some best practices for back-end development?
Back-end best practices include maintaining clean code, conducting regular code reviews, comprehensive testing, and thorough documentation.
Q14: What tools are essential for back-end developers?
Popular tools include Git for version control, Docker for containerization, Postman for API testing, and Jenkins for CI/CD.
Q15: What are the career options in back-end development?
Career options range from back-end developer roles to specialized positions like DevOps Engineer and Full-Stack Developer, each requiring specific skills and knowledge.
Q16: What are the emerging trends in back-end development?
Emerging trends include AI integration, serverless architecture, and DevOps, all of which enhance back-end functionality, scalability, and development efficiency.

